Technetium(VII) oxide
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Technetium(VII) oxide
|
|
| Other names
Technetium heptoxide
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
12165-21-8 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| PubChem | 22227441 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| Tc2O7 | |
| Molar mass | 307.810 g/mol |
| Appearance | light yellow solid |
| Density | 3.5 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 119.5 °C (247.1 °F; 392.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 310.6 °C (591.1 °F; 583.8 K) |
| hydrolysis to HTcO4 | |
| −40.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| orthrhombic | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | radioactive |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
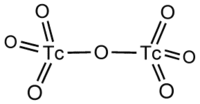
Technetium(VII) oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Tc2O7. This yellow volatile solid is a rare example of a molecular binary metal oxide, the other examples being RuO4, OsO4, and the unstable Mn2O7. It adopts a centrosymmetric corner-shared bi-tetrahedral structure in which the terminal and bridging Tc-O bonds are 167pm and 184 pm respectively and the Tc-O-Tc angle is 180°.
Technetium(VII) oxide is prepared by the oxidation of technetium at 450–500 °C:
It is the anhydride of pertechnic acid and the precursor to sodium pertechnetate:
...
Wikipedia
