Temporal muscle
| Temporalis | |
|---|---|
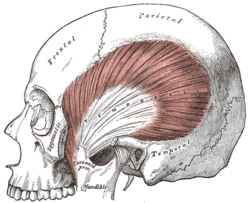
The temporalis; the zygomatic arch and masseter have been removed.
|
|
| Details | |
| Origin | Temporal lines on the parietal bone of the skull and the superior temporal surface of the sphenoid bone. |
| Insertion | Coronoid process of the mandible. |
| Artery | Deep temporal arteries |
| Nerve | Deep temporal nerves, branch(es) of the anterior division of the mandibular nerve (V3) |
| Actions | Elevation and retraction of mandible |
| Antagonist | Platysma muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus temporalis |
| TA | A04.1.04.005 |
| FMA | 49006 |
|
Anatomical terms of muscle
[]
|
|
The temporal muscle, also known as the temporalis, is one of the muscles of mastication. It is a broad, fan-shaped muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic arch so it covers much of the temporal bone.
In humans, it arises from the temporal fossa and the deep part of temporal fascia. It passes medial to the zygomatic arch and forms a tendon which inserts onto the coronoid process of the mandible, with its insertion extending into the retromolar fossa posterior to the most distal mandibular molar. In other mammals, the muscle usually spans the dorsal part of the skull all the way up to the medial line. There, it may be attached to a sagittal crest, as can be seen in early hominins like Paranthropus aethiopicus.
The temporal muscle is covered by the temporal fascia, also known as the temporal aponeurosis. This fascia is commonly used in tympanoplasty, or surgical reconstruction of the eardrum.
The muscle is accessible on the temples, and can be seen and felt contracting while the jaw is clenching and unclenching.
The temporalis is derived from the first pharyngeal arch in development.
As with the other muscles of mastication, control of the temporal muscle comes from the third (mandibular) branch of the trigeminal nerve. Specifically, the muscle is innervated by the deep temporal nerves.
The muscle receives its blood supply from the deep temporal arteries which anastomose with the middle temporal artery.
...
Wikipedia
