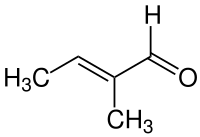
Trans-2-Methyl-2-butenal
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-2-Methylbut-2-enal
|
|
| Other names
(E)-2-Methylbut-2-enal
trans-2-Methyl-2-butenal trans-2,3-Dimethylacrolein Tiglic aldehyde Tiglinaldehyde Tiglaldehyde |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.122 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C5H8O | |
| Molar mass | 84.12 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.871 |
| Melting point | −78 °C (−108 °F; 195 K) |
| Boiling point | 116 to 119 °C (241 to 246 °F; 389 to 392 K) (752 mm Hg) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 65 °C (149 °F; 338 K) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related alkenals
|
Citral |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
trans-2-Methyl-2-butenal is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH=C(CH3)CHO. This colorless liquid is a building block in organic synthesis. It is an α,β-unsaturated aldehyde related to the better-known crotonaldehyde. The European rabbit, Oryctolagus cuniculus, uses 2-methyl-2-butenal as a pheromone. The rabbit pheromone, trans-2-methyl-2-butenal, was reported to be involved in the communication between species, defined under the class of "interomone."
...
Wikipedia
