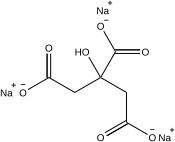
Trisodium citrate
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC names
Trisodium citrate
Trisodium 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate |
|
| Other names
Citrosodine
Citric acid, trisodium salt Sodium citrate E331 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.614 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | GE8300000 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| Na3C6H5O7 | |
| Molar mass | 258.06 g/mol (anhydrous), 294.10 g/mol (dihydrate) |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.7 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | >300 °C hydrates lose water ca. 150 C |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Pentahydrate form: 92 g/100 g H2O (25 °C) | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
1548 mg/kg (intraperitoneal, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Monosodium citrate Disodium citrate Calcium citrate Citric acid |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Trisodium citrate has the chemical formula of Na3C6H5O7. It is sometimes referred to simply as sodium citrate, though sodium citrate can refer to any of the three sodium salts of citric acid. It possesses a saline, mildly tart flavor. It is mildly basic and can be used along with citric acid to make biologically compatible buffers.
Sodium citrate is chiefly used as a food additive, usually for flavor or as a preservative. Its E number is E331. Sodium citrate is employed as a flavoring agent in certain varieties of club soda. Sodium citrate is common as an ingredient in Bratwurst, and is also used in commercial ready to drink beverages and drink mixes, contributing a tart flavor. It is found in gelatin mix, ice-cream, jams, sweets, milk powder, processed cheeses, carbonated beverages, and wine.
Sodium Citrate can also be used as an emulsifier for oils when making cheese. Sodium citrate allows the cheeses to melt without becoming greasy. Consider the following quote from modernist cuisine: "Our modernist version of mac and cheese owes its chemistry to James L. Kraft, who in 1916 patented the first American cheese slice. He showed that sodium phosphate keeps the water and fat droplets mixed when the cheese is melted. We use sodium citrate, which has the same effect and is easier to find. The resulting texture is as smooth as melted American cheese, but as complex and intense in flavor as any of your favorite cheeses."
As a conjugate base of a weak acid, citrate can perform as a buffering agent or acidity regulator, resisting changes in pH. Sodium citrate is used to control acidity in some substances, such as gelatin desserts. It can be found in the mini milk containers used with coffee machines. The compound is the product of antacids, such as Alka-Seltzer, when they are dissolved in water. The pH of a solution of 5 g/100 ml water at 25 °C is 7.5 – 9.0.
...
Wikipedia

