Ukrainian Language
| Ukrainian | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Pronunciation | [ukrɑˈjiɲsʲkɐ ˈmɔwɐ] |
| Native to | Ukraine |
| Ethnicity | Ukrainians |
|
Native speakers
|
45 million (2007) |
|
Indo-European
|
|
|
Early forms
|
Old East Slavic
|
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
|
|
Recognised minority
language in |
|
| Regulated by | National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine: Institute for the Ukrainian Language, Ukrainian language-information fund, Potebnya Institute of Language Studies |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | uk |
| ISO 639-2 | |
| ISO 639-3 | |
| Glottolog |
ukra1253 (Ukrainian)
|
| Linguasphere |
|

Ukrainian-speaking world
|
|
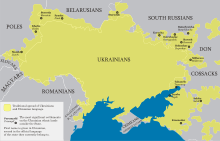
Ukrainian language and Ukrainians with their neighbors in the early 20th century.
|
|
Ukrainian ![]() i/juːˈkreɪniən/ (українська мова ukrayins'ka mova, pronounced [ukrɑˈjiɲsʲkɐ ˈmɔwɐ]) is an East Slavic language. It is the official state language of Ukraine and first of two principal languages of Ukrainians; it is one of the three official languages in the unrecognized state of Transnistria, the other two being Moldovan and Russian. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic script (see Ukrainian alphabet).
i/juːˈkreɪniən/ (українська мова ukrayins'ka mova, pronounced [ukrɑˈjiɲsʲkɐ ˈmɔwɐ]) is an East Slavic language. It is the official state language of Ukraine and first of two principal languages of Ukrainians; it is one of the three official languages in the unrecognized state of Transnistria, the other two being Moldovan and Russian. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic script (see Ukrainian alphabet).
Until the 20th century it was known in Russia as the Little-Russian dialect (Russian: малорусское наречие, малороссийский язык) from the Tsardom of Muscovy and later the Russian Empire, while in Poland and in Austria-Hungary as the Rusyn language or Ruthenian language (Polish: język ruski, rusiński, German: ruthenische Sprache).
...
Wikipedia
