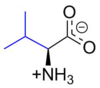
Valine
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Valine
|
|||
| Other names
2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
516-06-3 72-18-4 (L-isomer) 640-68-6 (D-isomer) |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:57762 |
||
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL43068 |
||
| ChemSpider |
6050 |
||
| DrugBank |
DB00161 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.703 | ||
| EC Number | 208-220-0 | ||
| 4794 | |||
| KEGG |
D00039 |
||
| PubChem | 1182 | ||
| UNII |
4CA13A832H |
||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C5H11NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 117.15 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.316 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 298 °C (568 °F; 571 K) (decomposition) | ||
| soluble | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.32 (carboxyl), 9.62 (amino) | ||
| -74.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Supplementary data page | |||
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|||
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Valine (abbreviated as Val or V) encoded by the codons GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isopropyl variable group, classifying it as a non-polar amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it and thus it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are any proteinaceous foods such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes.
Along with leucine and isoleucine, valine is a branched-chain amino acid. In sickle-cell disease, valine substitutes for the hydrophilic amino acid glutamic acid in β-globin. Because valine is hydrophobic, the hemoglobin is prone to abnormal aggregation.
Valine was first isolated from casein in 1901 by Hermann Emil Fischer. The name valine comes from valeric acid, which in turn is named after the plant valerian due to the presence of the acid in the roots of the plant.
According to IUPAC, carbon atoms forming valine are numbered sequentially starting from 1 denoting the carboxyl carbon, whereas 4 and 4' denote the two terminal methyl carbons.
...
Wikipedia