Ventilation perfusion scan
| Ventilation/perfusion scan | |
|---|---|
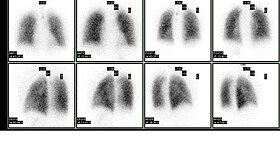
Normal pulmonary ventilation and perfusion (V/Q) scan. The nuclear medicine V/Q scan is useful in the evaluation of pulmonary embolism.
|
|
| OPS-301 code | 3-703.2 |
A ventilation/perfusion lung scan, also called a V/Q lung scan, is a type of medical imaging using scintigraphy and medical isotopes to evaluate the circulation of air and blood within a patient's lungs, in order to determine the ventilation/perfusion ratio. The ventilation part of the test looks at the ability of air to reach all parts of the lungs, while the perfusion part evaluates how well blood circulates within the lungs. As Q in physiology is the letter used to describe bloodflow the term V/Q scan emerged.
This test is most commonly done in order to check for the presence of a blood clot or abnormal blood flow inside the lungs (such as a pulmonary embolism (PE) although computed tomography with radiocontrast is now more commonly used for this purpose. The V/Q scan may be used in some circumstances where radiocontrast would be inappropriate, as in renal failure.
A V/Q lung scan may be performed in the case of serious lung disorders such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pneumonia as well as a lung performance quantification tool pre- and post-lung lobectomy surgery.
Decreased uptake of the inhaled radioisotope may indicate an impaired ability to breathe, airway obstruction, or possible pneumonia.
Decreased circulation of the injected MAA indicates a problem with blood flow into or within the lungs. A localized area of decreased uptake, usually in a wedge shaped (or pie shaped) configuration with normal ventilation images (mismatched defect) suggests a pulmonary embolus or blood clot in the lungs, which leads to reduced perfusion beyond the obstruction.
...
Wikipedia
