Ventricular drain
| External ventricular drain | |
|---|---|
| Intervention | |
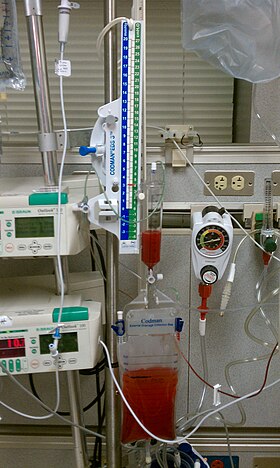
Drainage system showing bloody CSF due to intracranial hemorrhage.
|
An external ventricular drain (EVD), also known as a ventriculostomy or extraventricular drain, is a device used in neurosurgery to treat hydrocephalus and relieve elevated intracranial pressure when the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the brain is obstructed. An EVD is a flexible plastic catheter placed by a neurosurgeon or neurointensivist and managed by intensive care unit (ICU) physicians and nurses. The purpose of external ventricular drainage is to divert fluid from the ventricles of the brain and allow for monitoring of intracranial pressure. An EVD must be placed in a center with full neurosurgical capabilities, because immediate neurosurgical intervention can be needed if a complication of EVD placement, such as bleeding, is encountered.
EVDs are a short-term solution to hydrocephalus, and if the underlying hydrocephalus does not eventually resolve, it may be necessary to convert the EVD to a cerebral shunt, which is a fully internalized, long-term treatment for hydrocephalus.
The EVD catheter is most frequently placed by way of a twist-drill craniostomy placed at Kocher's point, a location in the frontal bone of the skull, with the goal of placing the catheter tip in the frontal horn of the lateral ventricle or in the third ventricle. The catheter is typically inserted on the right side of the brain, but in some cases a left-sided approach is used, and in other situations catheters are needed on both sides. EVDs can be used to monitor intracranial pressure in patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI), subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), or other brain abnormalities that lead to increased CSF build-up. In draining the ventricle, the EVD can also remove blood products from the ventricular spaces. This is important because blood is an irritant to brain tissue and can cause complications such as vasospasm.
...
Wikipedia
