Zarzal
| Zarzal, Valle del Cauca | |
|---|---|
| City | |
| City of Zarzal, Valle del Cauca | |
 |
|
| Nickname(s): "Sweet Land of Colombia", "The Z" | |
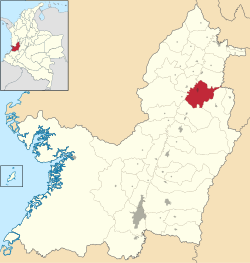 Location of the town and municipality of Zarzal in Valle del Cauca Department. |
|
| Location in Colombia | |
| Coordinates: 4°23′54″N 76°04′38″W / 4.39833°N 76.07722°W | |
| Country |
|
| Department | Valle del Cauca |
| Region | Andean |
| Demonym | Zarzaleno |
| Foundation | April 1, 1909 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Maria Alejandra Perdomo |
| Area | |
| • Total | 362 km2 (140 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 916 m (3,005 ft) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 43,035 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (310/sq mi) |
| Website |
www.valledelcauca.gov.co/zarzal |
| * | |
Zarzal (Spanish pronunciation: [saɾˈsal]) is a town and municipality in the north of the department of Valle del Cauca in Colombia. Its economy is based primarily on the extensive cultivation of sugar cane, on small and medium enterprises in the metallurgic sector, and on utilities. Commerce is also of great importance, because a great number of warehouses for basic necessity goods exist in the city. A marketplace also exists, which serves as reference for various cities that are close by. Zarzal has a population of about 50,000 inhabitants. New city districts were constructed in the center of the city; it has now become difficult to find bare land inside the city.
The territory is mostly flat within the valley of the Cauca River, a river that flows into La Paila River. The municipality is also home to the forest of the Caracolíes, Los Chorros, Cumba recreational park, La Paila river, Mount Caré and Mount Pan de Azúcar.
The municipality of Zarzal is one of the region with most production of sugar cane and sugar refineries. The municipality is home to two major companies; the Rio Paila Sugar Company and the Colombina Candy Factory.
Besides the cane and sugar production other agricultural products are produced in the municipality: plantain, yuca, cotton, maize, sorghum, sugar cane, soy, grapes, papaya, passion fruit, pitaya, citrics like oranges and limes, mango, guava, avocado and chontaduro. Some 200 square kilometres (77 sq mi) are used for cattle raising and 0.1 km2 (0.039 sq mi) for a small industrial fishing industry that produces tilapia, cachama, peacock bass and bocachico.
...
Wikipedia