| 1986 Pacific typhoon season |
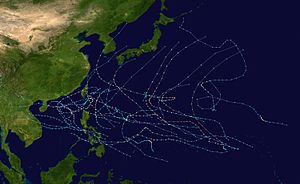
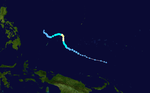
Season summary map
|
| Seasonal boundaries |
| First system formed |
January 29, 1986 |
| Last system dissipated |
January 3, 1987 |
| Strongest storm |
|
| Name |
Peggy |
| • Maximum winds |
205 km/h (125 mph)
(10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure |
900 hPa (mbar) |
|
| Seasonal statistics |
| Total depressions |
48 |
| Total storms |
29 |
| Typhoons |
19 |
| Super typhoons |
3 |
| Total fatalities |
>905 |
| Total damage |
> $508.5 million (1986 USD) |
| Related articles |
|
|
Pacific typhoon seasons
1984, 1985, 1986, 1987, 1988
|
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
February 1 – February 6 |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min) 970 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
April 26 – May 3 |
| Peak intensity |
120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 17 – May 23 |
| Peak intensity |
220 km/h (140 mph) (10-min) 910 hPa (mbar) |
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 21 – May 29 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 992 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 21 – June 25 |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min) 955 hPa (mbar) |
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 28 – July 2 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 985 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 3 – July 11 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min) 900 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 13 – July 17 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min) 955 hPa (mbar) |
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 20 – July 24 |
| Peak intensity |
65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min) 996 hPa (mbar) |
The 1986 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1986, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Tropical Storms formed in the entire west pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names.
A total of 32 tropical depressions formed in 1986 in the Western Pacific over an eleven-month time span. Of the 32, 30 became tropical storms, 19 storms reached typhoon intensity, and 3 reached super typhoon strength. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center considered Vera as two tropical cyclones, when all the warning centers treated Vera as one in real time, while another, Georgette, originated in the Eastern Pacific. Six of the tropical cyclones formed in August, which was the busiest month of the season. Eight tropical cyclones moved through the Philippines this season. Most of the deaths attributed to typhons in 1986 were caused by Peggy and Wayne
Of the thirty tropical storms formed in 1986 in the Western Pacific (from 32 tropical depressions), 19 reached typhoon intensity, and three reached super typhoon strength. Broken down by month, one tropical cyclone formed in February, one in April, two in May, three in June, three in July, seven in August, three in September, four in October, six in November, and two forming in December. Vera was considered two tropical cyclones by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center after the fact, though it was operationally treated as one system, and Georgette, was a former Eastern Pacific cyclone. Eight tropical cyclones moved through the Philippines this season, while three struck mainland China, one struck Korea, and one crossed the Japanese coast. Peggy and Wayne accounted for a majority of the death toll this season. Tropical cyclones accounted for 35 percent of the annual rainfall in Hong Kong this year.
The initial disturbance formed within two degrees of the equator within the monsoon trough on January 25. Over succeeding days, the thunderstorm area increased in size. However, it decreased significantly on January 30. As the convective area moved slowly westward, it increased in coverage once more, organizing into a tropical depression on February 1. Moving on a parabolic course east of the Philippines, Judy gained tropical storm status on February 2, and typhoon strength on February 4 after recurving to the northwest of the subtropical ridge. As westerly winds increased aloft, vertical wind shear weakened Judy back into a tropical storm, which lost tropical characteristics on February 6. After drifting slightly more east-northeastward, the low pressure area dissipated.
...
Wikipedia