2008 Pacific typhoon season
| 2008 Pacific typhoon season |
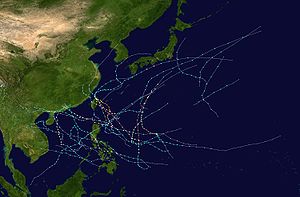
Season summary map
|
| Seasonal boundaries |
| First system formed |
January 13, 2008 |
| Last system dissipated |
December 18, 2008 |
| Strongest storm |
|
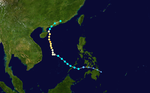
| Name |
Jangmi |
| • Maximum winds |
215 km/h (130 mph)
(10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure |
905 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics |
| Total depressions |
40 |
| Total storms |
22 |
| Typhoons |
11 |
| Super typhoons |
3 (unofficial)
|
| Total fatalities |
1,936 |
| Total damage |
$5.97 billion (2008 USD) |
| Related articles |
|
|
Pacific typhoon seasons
2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010
|
| Tropical depression (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
January 13 – January 18 |
| Peak intensity |
55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min) 1004 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
April 13 – April 20 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min) 960 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 7 – May 13 |
| Peak intensity |
195 km/h (120 mph) (10-min) 915 hPa (mbar) |
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 14 – May 17 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 992 hPa (mbar) |
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 14 – May 20 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min) 970 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 26 – June 3 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (10-min) 930 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 17 – June 25 |
| Peak intensity |
165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min) 945 hPa (mbar) |
| Tropical depression (JMA) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 4 – July 8 |
| Peak intensity |
55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min) 1000 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 13 – July 20 |
| Peak intensity |
120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min) 970 hPa (mbar) |
The 2008 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it runs year-round in 2008, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the International Date Line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 2008 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical storms formed in the entire Western North Pacific basin are assigned a name by the Japan Meteorological Agency. Tropical depressions formed in this basin are given a number with a "W" suffix by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center. In addition, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones (including tropical depressions) that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility. These names, however, are not in common use outside of the Philippines.
Each season several national meteorological services and scientific agencies forecast either the expected amount tropical cyclones, tropical storms, and typhoons forming in a season and/or how many tropical cyclones will affect a country or territory.
Since the 2000 typhoon season, the Laboratory for Atmospheric Research or the Guy Carpenter Asia-Pacific Climate Impact Centre (GCACIC), both of the City University of Hong Kong have issued forecasts of activity for each upcoming typhoon season. Forecasts are issued in April and June of each year and predict how many tropical cyclones, tropical storms, and typhoons there will be in a season. This season, the GCACIC is predicting a slightly more active than usual season. An average season, according to the GCACIC, has 31 tropical cyclones, 27 named storms, and 17 typhoons. In its April forecast, the GCACIC predicted 33 total tropical cyclones, 30 named storms, and 19 typhoons before predicting the same number of systems, tropical storms, and typhoons in its June forecast.
...
Wikipedia