Adenotonsillectomy
| Adenoiditis | |
|---|---|
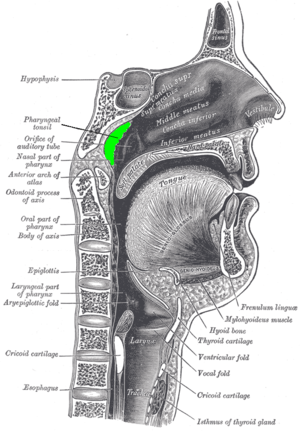 |
|
| Location of the adenoid | |
| Specialty | pulmonology |
Adenoiditis is the inflammation of the adenoid tissue, usually caused by an infection. Adenoiditis is treated using medication (antibiotics and/or steroids) or surgical intervention.
Adenoiditis may produce cold-like symptoms. However, adenoiditis symptoms often persist for ten or more days, and often include pus-like discharge from nose.
The infection cause is usually viral. However, if the adenoiditis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed for treatment. A steroidal nasal spray may also be prescribed in order to reduce nasal congestion. Severe or recurring adenoiditis may require surgical removal of the adenoids (adenotonsillectomy).
Acute adenoiditis is characterized by fever, runny nose, nasal airway obstruction resulting in predominantly oral breathing, snoring and sleep apnea, Rhinorrhea with serous secretion in viral forms and mucous-purulent secretion in bacterial forms. In cases due to viral infection symptoms usually recede spontaneously after 48 hours, symptoms of bacterial adenoiditis typically persist up to a week. Adenoiditis is sometimes accompanied by tonsillitis. Repeated adenoiditis may lead to enlarged adenoids.
Complications of acute adenoiditis can occur due to extension of inflammation to the neighboring organs.
Viruses that may cause adenoiditis include adenovirus, rhinovirus and paramyxovirus. Bacterial causes include , , Moraxella catarrhalis and various species of Staphylococcus including Staphylococcus aureus.
...
Wikipedia
