Albanian langage
| Albanian | |
|---|---|
| Shqip | |
| Pronunciation | [ʃcip] |
| Native to | Albania, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Greece and Albanian diaspora |
|
Native speakers
|
5.4 million (ca. 2011) |
|
Indo-European
|
|
| Dialects | |
|
Latin (Albanian alphabet) Albanian Braille |
|
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
|
|
Recognised minority
language in |
|
| Regulated by | Officially by the Social Sciences and Albanological Section of the Academy of Sciences of Albania |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | sq |
| ISO 639-2 |
alb (B)sqi (T)
|
| ISO 639-3 |
Individual codes: |
| Glottolog | alba1267 |
| Linguasphere | 55-AAA-aaa to 55-AAA-ahe (25 varieties) |
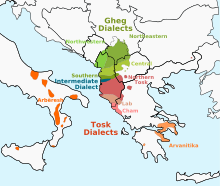
Albanian dialects
|
|
Albanian (shqip [ʃcip] or gjuha shqipe [ˈɟuha ˈʃcipɛ]) occupies an independent branch of the Indo-European language tree. It is the official language of Albania and Kosovo.
The language is spoken by over five million people, primarily in Albania, Kosovo, the Republic of Macedonia, but also in other areas of Southern Europe in which there is an Albanian population, including Montenegro and the Preševo Valley of southern Serbia.
Centuries-old communities speaking Albanian-based dialects can be found scattered in Croatia the Arbanasi, Greece the Arvanites and Cham, Southern Italy,Sicily, and Calabria the Arbëreshë and as well as in Ukraine. Due to the large Albanian diaspora, the total number of speakers is much higher than the native speakers in Southeast Europe.
The language is spoken by approximately 7 million people primarily in Greece, Italy, Kosovo, Macedonia and Montenegro. However, due to the large Albanian diaspora, the total number of speakers is much higher than the native speakers in Southern Europe.
...
Wikipedia
