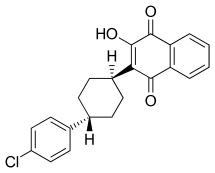
Atovaquone
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mepron |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a693003 |
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| ATC code | P01AX06 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Biological half-life | 2.2–3.2 days |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
95233-18-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 74989 |
| DrugBank |
DB01117 |
| ChemSpider |
10482034 |
| UNII |
Y883P1Z2LT |
| KEGG |
D00236 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:575568 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1450 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.158.738 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H19ClO3 |
| Molar mass | 366.837 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Atovaquone (alternative spelling: atavaquone) is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of naphthoquinones. Atovaquone is a hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, an analog of ubiquinone, with antipneumocystic activity. It is manufactured in the US in the liquid form, or oral suspension, under the brand name Mepron.
Atovaquone is a medication used to treat or prevent:
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX, Bactrim) is generally considered first-line therapy for PCP or toxoplasmosis. However, atovaquone may be used in patients who cannot tolerate, or are allergic to, sulfonamide medications such as TMP-SMX. In addition, atovaquone has the advantage of not causing myelosuppression, which is an important issue in patients who have undergone bone marrow transplantation.
Atovaquone, as a combination preparation with proguanil, has been commercially available from GlaxoSmithKline since 2000 as Malarone for the treatment and prevention of malaria.
...
Wikipedia
