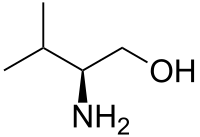
Valinol
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(S)-(+)-2-Amino-3-methyl-1-butanol
|
|
| Other names
(2S)-2-Amino-3-methyl-butan-1-ol
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C5H13NO | |
| Molar mass | 103.17 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to yellow crystalline powder |
| Density | 0.926 g/mL |
| Melting point | 30 to 34 °C (86 to 93 °F; 303 to 307 K) |
| Boiling point | 189 to 190 °C (372 to 374 °F; 462 to 463 K) |
| Very soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Sigma Aldrich |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P305+351+338 | |
| Flash point | 90°C closed cup |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Valinol is an organic compound named after, and commonly produced from, the amino acid valine. The compound is chiral and is produced almost exclusively as the S‑isomer (also designated as the L‑isomer), due to the abundant supply of S-valine. It is part of a broader class of amino alcohols.
Valinol can be generated by converting the carboxylic group of valine to an alcohol with a strong reducing agent such as lithium aluminium hydride, or with NaBH4 and I2 (forming the borane–tetrahydrofuran complex). In both cases the valinol produced can be subsequently purified by short path distillation.
Valinol is mainly used to prepare chiral oxazolines, a process which can be achieved via a variety of methods. These oxazolines are principally used as ligands in asymmetric catalysis.
...
Wikipedia
